最近想了解下SpringBoot启动流程,网上看了些博客,但是一般都很简单,看得我云里雾里,所以决定自己一行一行分析源码,目标是尽可能知道每一行代码的作用。
首先看下启动类,如下代码,一个main方法,很简单,主要是两部分,@SpringBootApplication注解和SpringApplication调用的run()方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @SpringBootApplication public class WjApplication public static void main (String[] args) SpringApplication.run(WjApplication.class, args); } }
上篇先讲下@SpringBootApplication注解,首先也看下源代码,然后一行行分析。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan( excludeFilters = {@Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class} ), @Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class} )} ) public @interface SpringBootApplication { @AliasFor( annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class ) Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; @AliasFor( annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class ) String[] excludeName() default {}; @AliasFor( annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages" ) String[] scanBasePackages() default {}; @AliasFor( annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses" ) Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {}; @AliasFor( annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "nameGenerator" ) Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class; @AliasFor( annotation = Configuration.class ) boolean proxyBeanMethods () default true }
1.@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) 这个注解属于Java基础内容,一个数组元素,看注释说:返回注释类型可以应用于的元素种类的数组,因此这个注释就是用于指定@SpringBootApplication注解可添加到的类型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Target { ElementType[] value(); }
{ElementType.TYPE}数组,只有一个元素,看下ElementType的源码,总共有10种,最后2种是JDK1.8新增的,然后TYPE类型,看注释可知用于Class, interface (including annotation type), enum。而我们上面的WjApplication就是Class类型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public enum ElementType TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE, ANNOTATION_TYPE, PACKAGE, TYPE_PARAMETER, TYPE_USE }
2.@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 该注解还是Java基础,看注释,返回一个保留策略,也就是说指定当前被修饰的注解会被保留多久
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Retention { RetentionPolicy value () ; }
看下参数RetentionPolicy源码,总共3中类型,RUNTIME看注释:注解会被编译器记录在Class文件中,运行时也会被虚拟机保存,可以通过反射获取。这种类型是保留时间最长的,和普通的类是一样的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public enum RetentionPolicy SOURCE, CLASS, RUNTIME }
3.@Documented 还是Java基础,添加这个注解后生成javadoc的时候会被记录。
1 2 3 4 5 @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Documented {}
4.@Inherited 看名字就可以知道,添加该注解后,注释会被自动继承,也就是说,如果有一个类继承了WjApplication,那么这个类也会带@SpringBootApplication注解。
1 2 3 4 5 @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Inherited {}
5.@SpringBootConfiguration 这个注解是SpringBoot特有的,主要分析@Configuration和@AliasFor注解。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Configuration public @interface SpringBootConfiguration { @AliasFor( annotation = Configuration.class ) boolean proxyBeanMethods () default true }
(1)@AliasFor 由@Target({ElementType.METHOD})可知该注解用于方法上。该注解主要有两个功能,添加别名和组合注解。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) @Documented public @interface AliasFor { @AliasFor("attribute") String value () default "" ; @AliasFor("value") String attribute () default "" ; Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class; }
a.添加别名 如下代码,path和value属性都互为别名,也就是说在使用这个注解的时候,参数写value = xx或者path = xx的效果是一样的。
注意:
互为别名的属性属性值类型,默认值,都是相同的;
互为别名的注解必须成对出现,比如 value 属性添加了@AliasFor("path"),那么 path 属性就必须添加@AliasFor("calue");
另外还有一点,互为别名的属性必须定义默认值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Mapping public @interface RequestMapping { String name () default "" ; @AliasFor("path") String[] value() default {}; @AliasFor("value") String[] path() default {}; ... }
b.组合注解 如下代码,设置annotation = ComponentScan.class和attribute = "basePackages"就代表给@ComponentScan注解的basePackages属性设置scanBasePackages别名,这样就可以加多个注解组合成一个注解。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ... @AliasFor( annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class ) String[] excludeName() default {}; @AliasFor( annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages" ) String[] scanBasePackages() default {}; ...
(2)@Configuration 用于定义一个配置类,同时也是一个bean,因为有@Component注解。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Component public @interface Configuration { @AliasFor( annotation = Component.class ) String value () default "" ; boolean proxyBeanMethods () default true }
@Component注解,看下代码,该注解用于声明当前类作为Spring容器的bean
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Indexed public @interface Component { String value () default "" ; }
@Indexed源码,这个注解简单来讲就是能给bean生成索引,提高SpringBoot启动时扫描bean文件的速度。它是如何提高的以后有机会再分析。
1 2 3 4 5 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Indexed {}
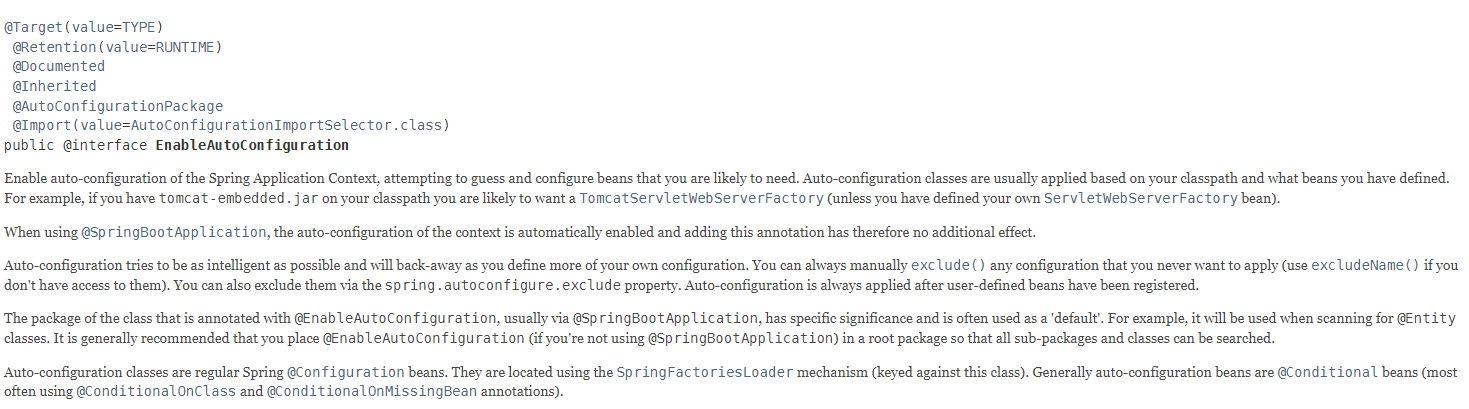
6.@EnableAutoConfiguration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration" ; Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; String[] excludeName() default {}; }
看下官方API文档 的介绍,第一句话就介绍了这个注解的作用:通过用户配置的classpath自动加载可能需要的bean。
ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY : 环境参数,当自动配置被启动时可以被重写。
exclude :设置不需要自动配置的类
excludeName :设置不需要自动配置的类名
(1)@AutoConfigurationPackage 注册自动扫描的包,如果没有声明基础包路径,则以当前注解所在的包作为自动扫描的包
basePackages:字符串数组,设置基础包路径
basePackageClasses:Class数组,设置基础包路径
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @Import({Registrar.class}) public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage { String[] basePackages() default {}; Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {}; }
(2)@Import 用于导入一些配置类,功能同Spring的xml文件配置中的<import>标签,Spring提供三种方式让类可以被import,被import的类会生成bean被Spring容器管理。
带@Configuration注解的类(4.2版本后也可以是普通类)
继承ImportSelector接口
继承ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Import { Class<?>[] value(); }
了解了@Import,再稍微了解下前面@EnableAutoConfiguration引入的AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class和@AutoConfigurationPackage引入的Registrar.class
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class:该类主要的作用是加载META-INF/spring.factories中的bean到容器中,后面在介绍SpringBoot自动加载原理的时候再详细分析。Registrar.class:该类为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationPackages类的一个内部类AutoConfigurationPackages官方文档解释为:保存自动配置类以供使用。Registrar的作用是批量注册某一个包下的所有组件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public abstract class AutoConfigurationPackages ... static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar , DeterminableImports Registrar() { } public void registerBeanDefinitions (AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) AutoConfigurationPackages.register(registry, (String[])(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImports(metadata)).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0 ])); } public Set<Object> determineImports (AnnotationMetadata metadata) return Collections.singleton(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImports(metadata)); } } }
这样,SpringBoot启动类的注解就简单的分析完了,基本上是和SpringBoot的自动配置有关,SpringBoot的自动配置后面会详细分析原理。下一篇文章将会分析启动类的main方法。